Flanges are essential for making safe, leak-proof connections between pipes, valves, pumps, and other equipment in piping systems. ANSI B16.5 is one of the most well-known and often utilized standards for flanges in industries across the globe. This blog post will assist you in comprehending the essential features of ANSI B16.5 flanges, regardless of your background—engineer, procurement professional, or just someone curious about piping components.
What is ANSI B16.5?
The American National Standards Institute (ANSI) created ANSI B16.5, a standard that details the measurements, composition, pressure ratings, and tolerances for pipe flanges and flanged fittings. It applies to flanges used in a variety of industries and covers flanges with nominal pipe sizes ranging from NPS ½” to NPS 24″.
Key Features of ANSI B16.5 Flanges
1. Pressure Ratings
ANSI B16.5 flanges are classified into seven pressure classes: 150, 300, 400, 600, 900, 1500, and 2500. These ratings indicate the maximum pressure the flange can withstand at a specific temperature. For example, a Class 150 flange can handle lower pressures compared to a Class 2500 flange, which is designed for extremely high-pressure applications.
2. Flange Types
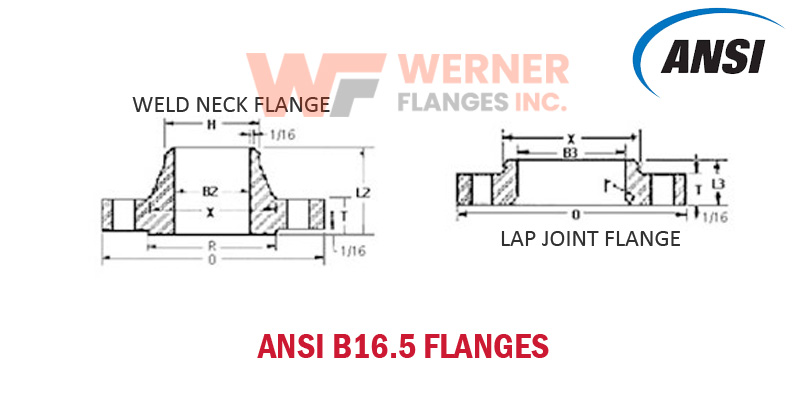
ANSI B16.5 defines several types of flanges, each suited for specific applications:
- Weld Neck Flange: Ideal for high-pressure and high-temperature applications due to its tapered hub and strong connection.
- Slip-On Flange: Easy to install and suitable for low-pressure systems.
- Socket Weld Flange: Used for small-diameter, high-pressure piping systems.
- Threaded Flange: Attaches to pipes without welding, making it ideal for low-pressure systems.
- Blind Flange: Used to seal the end of a piping system.
- Lap Joint Flange: Paired with a stub end for systems requiring frequent disassembly.
3. Materials
ANSI B16.5 flanges are made from a variety of materials, including:
- Carbon steel
- Stainless steel
- Alloy steel
- Duplex stainless steel
- Nickel alloys
The material selection depends on the fluid being transported, operating temperature, and pressure conditions.
4. Dimensions
The standard provides detailed dimensions for each flange size and pressure class, including:
- Outer diameter
- Bolt circle diameter
- Number of bolt holes
- Thickness
These dimensions ensure compatibility and interchangeability across different manufacturers.
5. Facing Types
Flanges have different facing types to accommodate gaskets and ensure a proper seal:
- Raised Face (RF): The most common type, featuring a small raised area around the bore for gasket placement.
- Flat Face (FF): Used for low-pressure applications where the gasket sits on the entire face.
- Ring-Type Joint (RTJ): Designed for high-pressure and high-temperature applications, using a metal ring gasket.
How to Select the Right ANSI B16.5 Flange
Choosing the correct flange for your application is crucial for ensuring safety and efficiency. Here’s a step-by-step guide:
- Determine Pressure and Temperature Requirements: Identify the operating pressure and temperature of your system to select the appropriate pressure class (e.g., Class 150, Class 300, etc.).
- Choose the Flange Type: Select the flange type based on your application. For example, use a weld neck flange for high-pressure systems or a slip-on flange for low-pressure systems.
- Select the Material: Choose a material that is compatible with the fluid and operating conditions. For corrosive environments, stainless steel or nickel alloys may be required.
- Match the Pipe Size: Ensure the flange size matches the nominal pipe size (NPS) of your piping system.
- Consider the Facing Type: Select the facing type based on the gasket and sealing requirements. Raised face is the most commonly used.
Installation Best Practices
Proper installation is key to ensuring a leak-proof and long-lasting connection. Follow these tips:
- Align the Flanges Properly: Misalignment can lead to leaks and stress on the piping system.
- Use the Correct Gasket: Choose a gasket material that can withstand the operating conditions.
- Tighten Bolts Evenly: Use a cross-pattern tightening sequence to ensure even pressure distribution.
- Inspect Before Installation: Check for any damage or defects in the flange or gasket before installation.
Applications of ANSI B16.5 Flanges
ANSI B16.5 flanges are used in a wide range of industries, including:
- Oil and Gas: For connecting pipelines, valves, and pumps in refineries and offshore platforms.
- Chemical Processing: In systems handling corrosive or hazardous fluids.
- Power Generation: For high-temperature and high-pressure steam systems.
- Water Treatment: In pipelines transporting water and wastewater.
Why Choose ANSI B16.5 Flanges?
ANSI B16.5 flanges are preferred for their:
- Standardization: Ensures compatibility and interchangeability.
- Versatility: Suitable for a wide range of applications and industries.
- Reliability: Designed to withstand high pressures and temperatures.
- Global Acceptance: Widely recognized and used worldwide.
Werner Flanges is a prominent manufacturer of ANSI B16.5 flanges. Contact us today or send an email to sales@wernerflanges.com for latest pricing.